Cardiovascular Health
- Cardiovascular Health Home
- CVH Data and Trends
- CVH Programs & Resources
- Minnesota 2035 Plan
- Minnesota Stroke Program
- About Us
Learn More
Related Topics
Contact Info
Cardiovascular Health Program
Cardiovascular Health Indicator
Measure: Controlling High Blood Pressure
| Indicator | Date of Most Recent Measure | Current Measure | Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
| Percentage of patients ages 18-85 with a diagnosis of hypertension, or high blood pressure, whose blood pressure was adequately controlled | 2020 | 62.3% | Getting Worse |
Overview
- In 2020, almost two out of three Minnesotans aged 18-85 with diagnosed high blood pressure had their blood pressure under control.
- The first year of the COVID-19 pandemic impacted the ability for many patients to access primary care, their providers, and sometimes their medications; these are just some of the reasons that blood pressure control declined sharply in 2020.
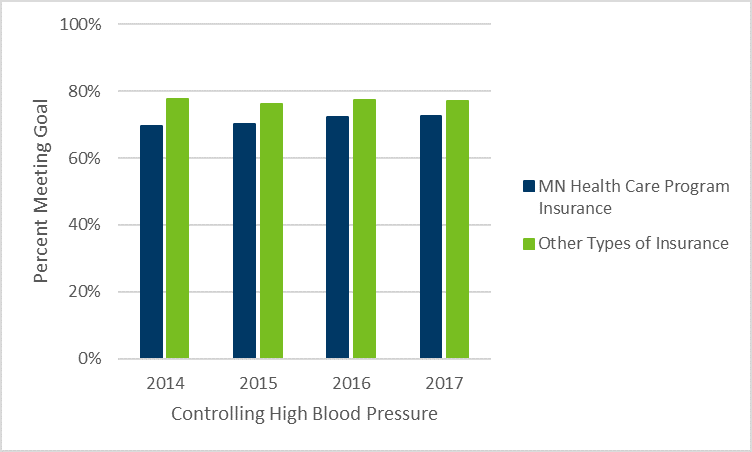
- Patients with Minnesota Health Care Program insurance are less likely to have their blood pressure under control compared to individuals with other types of insurance, but this gap has narrowed.
- Black/African American patients with Minnesota Health Care Program insurance are less likely to have their blood pressure under control compared to all adults with Minnesota Health Care Program insurance.
See Also:
Quick Facts about High Blood Pressure
Last Updated: 01/03/2023