Annual Summary of Disease Activity:
Disease Control Newsletter (DCN)
Related Topics
Contact Info
HIV Infection and AIDS, 2004
Surveillance for AIDS has been conducted in Minnesota since 1982. In 1985, when the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the first diagnostic test for HIV, Minnesota became the first state to make HIV infection a reportable condition; 39 states now require confidential reporting of HIV infection.
Compared to other states nationwide, the incidence of HIV/AIDS in Minnesota is moderately low. In 2003, state-specific AIDS incidence rates per 100,000 population ranged from 0.5 in North Dakota to 34.8 in New York, with 3.5 cases per 100,000 population reported in Minnesota. Similar comparisons for HIV (non-AIDS) incidence rates are not possible, because some states only began HIV (non-AIDS) reporting recently.
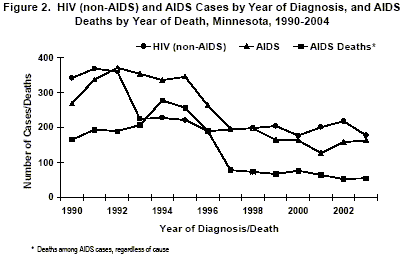
As of December 31, 2004, a cumulative total of 7,547 cases of HIV infection have been reported to MDH, including 4,334 AIDS cases and 3,213 HIV (non-AIDS) cases. Of these HIV/ AIDS case-patients, 2,697 (36%) are known to have died.
The annual number of AIDS cases reported in Minnesota increased steadily from the beginning of the epidemic through the early 1990s, reaching a peak of 370 cases in 1992. Beginning in 1996, the annual number of new AIDS diagnoses, and deaths among AIDS case-patients, declined sharply in Minnesota, primarily due to new antiretroviral therapies, which delay the progression from HIV infection to AIDS and improve survival. In 2004, 196 new AIDS cases and 58 deaths among AIDS patients were reported (Figure 2).
The annual number of newly diagnosed HIV (non-AIDS) cases reported in Minnesota has remained fairly constant since the mid-1990s, with 192 reported in 2004. This trend, coupled with improved survival, has led to an increasing number of persons in Minnesota living with HIV or AIDS. Approximately 5,000 persons with HIV/ AIDS were residing in Minnesota at the end of 2004.
Historically, and in 2004, nearly 90% (272/307) of new HIV infections (both HIV [non-AIDS] and AIDS at first diagnosis) reported in Minnesota occur in the Twin Cities metropolitan area. However, HIV or AIDS cases have been diagnosed in residents of more than 80% of counties statewide. HIV infection is most common in areas with higher population densities and greater poverty.
The majority of new HIV infections in Minnesota occur among males. Trends in the annual number of new HIV infections diagnosed among males differ by race/ethnicity. New infections occurred primarily among white males in the 1980s and early 1990s. Although whites still comprise the largest proportion of new HIV infections among males, the number of new infections in this population has decreased since 1991. In contrast to declining numbers of new HIV infections among white males, the decline among U.S.-born black males has been more gradual, falling from a peak of 81 new infections in 1992 to 40 new infections in 2004. The number of HIV infections diagnosed among Hispanic and African-born males has increased annually, with 24 new infections, among each group, diagnosed in 2004.
Females account for an increasing percentage of new HIV infections, from 10% of new infections in 1990 to 29% in 2004. Trends in HIV infections diagnosed annually among females also differ by race/ethnicity. Early in the epidemic, whites accounted for the majority of newly diagnosed infections in women. Since 1991, the number of new infections among women of color has exceeded that of white women. The annual number of new HIV infections diagnosed among U.S.-born black females has remained near 20 cases the past 4 years. During that same time the number of new infections among African-born females increased 25% to 35 cases in 2004, continuing a dramatic increase from just three cases in 1996. The annual number of new infections diagnosed among Hispanic, American Indian, and Asian females is small, with 10 or fewer cases annually in each group.
Despite relatively small numbers of cases, persons of color are disproportionately affected by HIV/AIDS in Minnesota. In 2004, non-white men comprised approximately 12% of the male population in Minnesota and 43% of new HIV infections among men. Similarly, persons of color comprised approximately 11% of the female population and 77% of new HIV infections among women. It bears noting that race is not considered a biological cause of disparities in the occurrence of HIV, but instead race is a marker for other risk factors, including lower socioeconomic status and education.
Since the beginning of the HIV epidemic, male-to-male sex has been the predominant mode of exposure to HIV reported in Minnesota, although the number and proportion of new HIV infections attributed to men who have sex with men (MSM) have declined since 1991. In 1991, 69% (324/470) of new HIV infections were attributed to MSM (or MSM who also inject drugs); by 2004, this percentage had decreased to 44% (134/307). However, current attitudes, beliefs, and unsafe sexual practices documented in surveys among MSM nationwide, and a current epidemic of syphilis among MSM, documented in Minnesota and elsewhere, warrant concern. Similar to syphilis increases in other U.S. cities and abroad, nearly 50% of the recent syphilis cases in Minnesota among MSM were co-infected with HIV, some for many years. “Burn out” from adopting safer sexual practices and exaggerated confidence in the efficacy of HIV treatments may be contributors to resurging risky sexual behavior among MSM. CDC recommends annual screening for sexually transmitted diseases (including HIV and syphilis) for sexually active MSM and more frequent screening for MSM who report sex with anonymous partners or in conjunction with drug use.
The number and percentage of HIV infections in Minnesota that are attributed to injection drug use have declined over the past decade for men and women, falling from 17% (80/470) of cases in 1991 to 4% (13/307) in 2004. Heterosexual contact with a partner who has or is at increased risk of HIV infection is the predominant mode of exposure to HIV for women. Eighty percent of 90 new HIV diagnoses among women in 2004 can be attributed to heterosexual exposure after re-distributing those with unspecified risk (Lansky A, et al. A method for classification of HIV exposure category for women without HIV risk information. MMWR 2001; 50[RR-6]:29-40).
Historically, race/ethnicity data for HIV/ AIDS in Minnesota have grouped U.S.-born blacks and African-born persons together as “black.” In 2001, MDH began analyzing these groups separately, and a marked trend of increasing numbers of new HIV infections among African-born persons was observed. In 2004, there were 59 new HIV infections reported among Africans. While African-born persons comprise less than 1% of the state’s population, they accounted for nearly 20% of all HIV infections diagnosed in Minnesota in 2004. Until recently, culturally specific HIV prevention messages have not been directed to African communities in Minnesota. Taboos and other cultural barriers make it challenging to deliver such messages and to connect HIV-infected individuals with prevention and treatment services. Collaborations between MDH, the Minnesota Department of Human Services, and community-based organizations serving African-born persons in Minnesota are underway addressing these complex issues.
- For up to date information see>> HIV (HIV/AIDS)
- Full issue>> Annual Summary of Communicable Diseases Reported to the Minnesota Department of Health, 2004