Annual Summary of Disease Activity:
Disease Control Newsletter (DCN)
Related Topics
Contact Info
Anaplasmosis, 2018
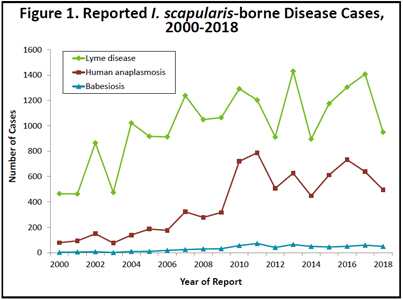
Anaplasmosis, caused by Anaplasma phagocytophilum, is transmitted by bites from Ixodes scapularis, the blacklegged tick. Although the organism that causes anaplasmosis was previously known by other names and thought to be a part of the genus Ehrlichia, anaplasmosis and ehrlichiosis (due to E. chaffeensis) are distinct diseases caused by different rickettsial species. The same tick vector also transmits the etiologic agents of Lyme disease, babesiosis, ehrlichiosis (due to E. muris), and Powassan virus. In rare circumstances, A. phagocytophilum may be transmitted by blood transfusion.
In 2018, 496 confirmed or probable cases (8.9 cases per 100,000 population) were reported, down from the 638 cases reported in 2017 (Figure 1). Despite some annual fluctuations in reported cases, the overall trend is an increase in yearly case totals over time, with a median of 627 cases reported per year since 2010. Sixty-two percent (307) of cases reported were male. The median age of cases was 61 years (range, 2 to 92), 17 years older than the median age of confirmed Lyme disease cases. As is typical, most cases had illness onsets during the summer months, with 72% of cases reporting illness onsets in June and July. In 2018, 132 (27%) cases were hospitalized for their infection, with a median duration of 4 days (range, 2 to 33 days).
- For up to date information see>> Anaplasmosis
- Full issue>> Annual Summary of Communicable Diseases Reported to the Minnesota Department of Health, 2018