Annual Summary of Disease Activity:
Disease Control Newsletter (DCN)
Related Topics
Contact Info
Campylobacteriosis, 2016
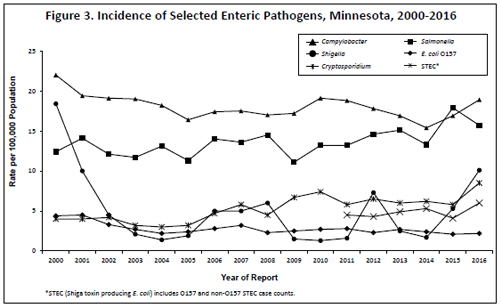
There were 1,042 culture-confirmed Campylobacter cases reported in 2016 (18.9 per 100,000 population). This is a 13% increase from the 925 cases reported in 2015, and a 15% increase from the annual median of 908 cases reported from 2006 to 2015 (range, 843 to 1,009). In 2016, 44% of cases occurred in people who resided in the metropolitan area. Of the 1,012 Campylobacter isolates confirmed and identified to species by MDH, 86% were C. jejuni and 8% were C. coli.
The median age of cases was 36 years (range, 1 month to 89 years). Forty-one percent were between 20 and 49 years of age, and 12% were ≤5 years of age. Fifty-five percent were male. Fifteen percent were hospitalized; the median length of hospitalization was 3 days. Forty-nine percent of infections occurred during June through September. Of the 947 cases for whom data were available, 163 (17%) reported travel outside the United States during the week prior to illness onset. The most common travel destinations were Europe (n=45), Mexico (n=38), Central or South America or the Caribbean (n=37), Asia (n=23), and Africa (n=13).
Five foodborne outbreaks were identified in 2016. In one outbreak, 2 culture-confirmed C. jejuni infections were associated with a deli. In a second outbreak, 2 culture-confirmed C. jejuni infections were associated with a restaurant. In another, 3 culture-confirmed C. coli cases were associated with a sushi restaurant. In another, 1 culture-confirmed case was associated with raw oysters sourced from Washington. Lastly, 2 cases with culture-confirmed C. jejuni infections were associated with duck hearts served at a restaurant. The vehicle of transmission was not confirmed for the first three outbreaks. An additional four outbreaks of C. jejuni infections were investigated in 2016. One outbreak was associated with environmental contamination at a poultry plant. The remaining three outbreaks were associated with a private farm, summer camp, and child care facility; however, the route of transmission was not determined.
A primary feature of public health importance among Campylobacter cases was the continued presence of isolates resistant to fluoroquinolone antibiotics (e.g., ciprofloxacin), which are commonly used to treat campylobacteriosis. In 2016, the overall proportion of quinolone resistance among Campylobacter isolates tested was 26%. However, 80% of Campylobacter isolates from patients with a history of foreign travel during the week prior to illness onset, regardless of destination, were resistant to fluoroquinolones. Fifteen percent of Campylobacter isolates from patients who acquired the infection domestically were resistant to fluoroquinolones.
In June 2009, a culture-independent test (CIDT) became commercially available for the qualitative detection of Campylobacter antigens in stool. In 2016, 572 patients were positive for Campylobacter by an antigen detection CIDT conducted in a clinical laboratory. However, only 193 (34%) of the specimens were subsequently culture-confirmed. Beginning in 2015, some clinical laboratories in Minnesota began testing stool specimens with PCR-based gastrointestinal pathogen panels, another type of CIDT. In 2016, 416 patients were positive for Campylobacter by a PCR gastrointestinal panel; 317 (76%) of these specimens were culture-confirmed. Only culture-confirmed cases met the surveillance case definition for inclusion in MDH case count totals.
- For up to date information see>> Campylobacteriosis (Campylobacter)
- Full issue>> Annual Summary of Communicable Diseases Reported to the Minnesota Department of Health, 2016