Advancing Stroke Care through Data Improvements
Stroke is the fifth leading cause of death and a major cause of disability in Minnesota. Because stroke treatment is highly time-sensitive, rapid administration of thrombolytic medications can significantly improve functional outcomes and reduce mortality. Coordinating stroke recognition and treatment across the entire continuum of care is essential.
Over the last 20 years, the Minnesota Department of Health (MDH) has expanded statewide efforts to reduce the burden of stroke, with a major focus on data collection and use in partnership with hospitals. The Minnesota Stroke Registry, established in 2008 through collaboration between the Minnesota Stroke Program and Minnesota IT Services (MNIT), serves as the foundation of this work. The Registry allows MDH and hospitals to collect, monitor, report, and use data to inform quality improvement in acute stroke care. All hospitals are required to submit case-level stroke data to MDH and meet Statewide Quality Reporting and Measurement System requirements through their submissions to the Registry.
Statewide expansion
From 2008 to 2025, the Registry data collection expanded from collecting data from 12 hospitals to 130.
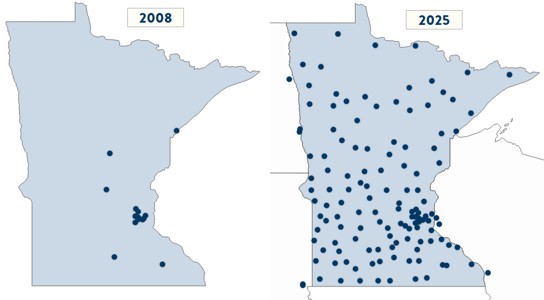
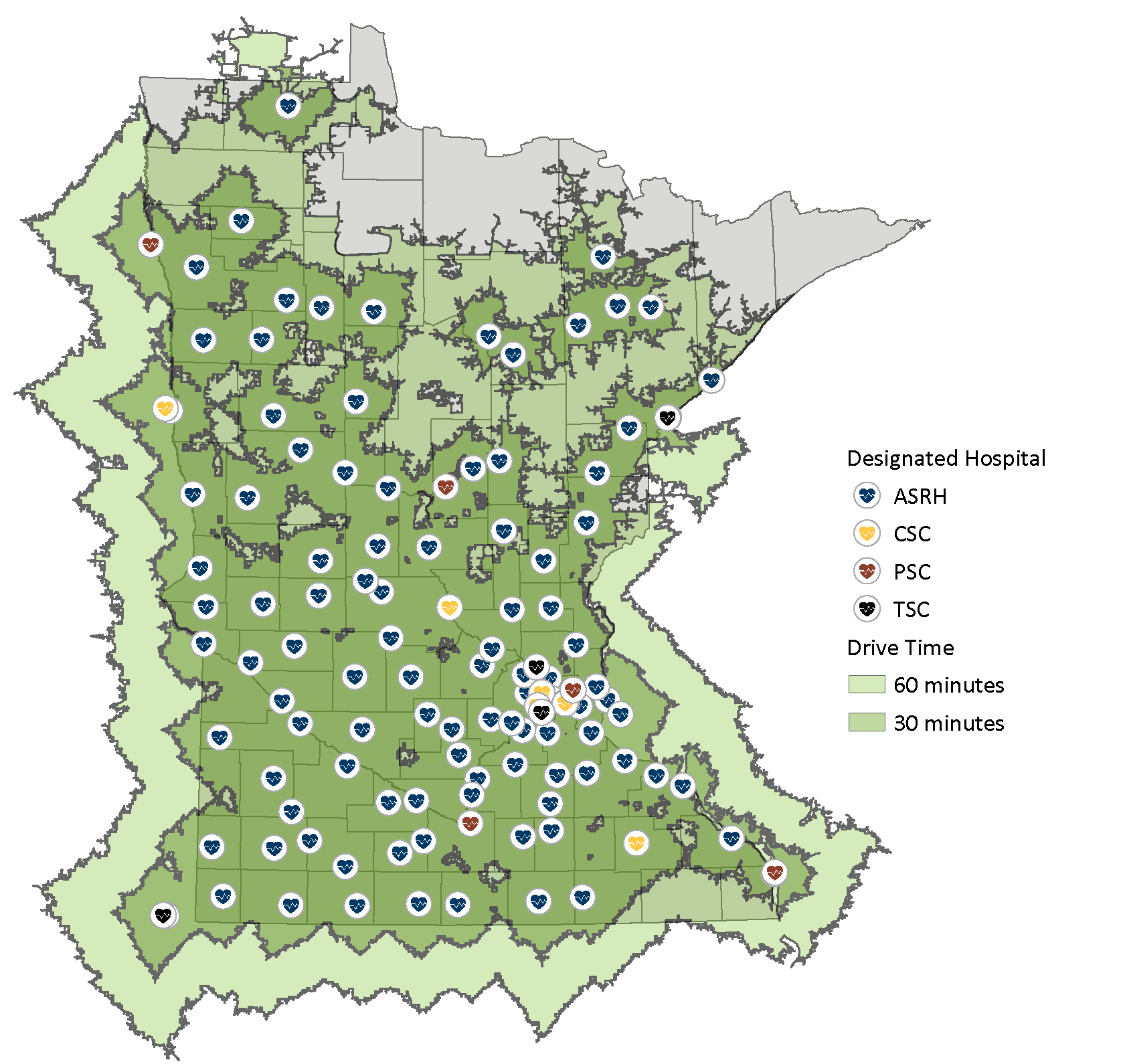
Additionally, stroke hospital designation has expanded from 11 hospitals in 2012 to 121 participating hospitals today. This means 97% of Minnesotans now live within 30 minutes of a designated stroke hospital.
A need for updates
Over time, hospital partners expressed a need for greater autonomy to use their data—particularly to identify trends and better understand how stroke affects the communities they serve.
At the same time, MNIT determined that the system had become outdated and required significant security updates to maintain the safety and integrity of the data. The enhancements and system upgrades needed to meet these requirements were estimated to be costly.
The technology modernization fund
The Minnesota Stroke Portal is the overarching electronic system that houses the Minnesota Stroke Registry, reporting features, stroke hospital designation applications, and key program resources. Updating the Minnesota Stroke Portal became critical to ensure MDH could continue supporting quality improvement, improving stroke outcomes, and maintaining secure, efficient data operations.
In 2023, the Minnesota Legislature appropriated $40 million over four years for the Technology Modernization Fund, allowing MNIT to invest in projects that modernize, secure, and improve the user experience of state technology systems. This funding opportunity arrived at exactly the right moment—allowing the Minnesota Stroke Program to propose leveraging existing infrastructure, modernizing processes, and aligning with internal data modernization efforts. In partnership with MNIT, the Stroke Program applied for and was awarded funds for system enhancements and upgrades.
Over the course of a year, the team completed a $350,000 project that included a full system rebuild, security enhancements, streamlined manual processes, improved integration across data systems, and an enhanced user experience. Key upgrades included:
- Expanded demographic options and report filters (e.g., race/ethnicity, insurance) to identify inequities and support more targeted improvement.
- Integration with the National Syndromic Surveillance Program to help identify cases and prepopulate corresponding data elements.
- New data visualizations and dashboards to track and share quality improvement progress using submitted data.
- Improved access to the data dictionary through tooltips within the Registry.
- New reports identifying patients who did not meet case measures or time goals to support efficient chart review.
- Enhanced data security and significant functional improvements.
- Streamlined manual processes to save valuable staff time.
- Integration across data systems through the statewide ImageTrend contract for AHA GWTG-Stroke users, enabling EMS data to flow directly into GWTG-Stroke.
- Business-side autonomy to make timely changes using content management features.
- Improved overall user experience and accessibility.
- Development of sustainable system management supported by detailed documentation.
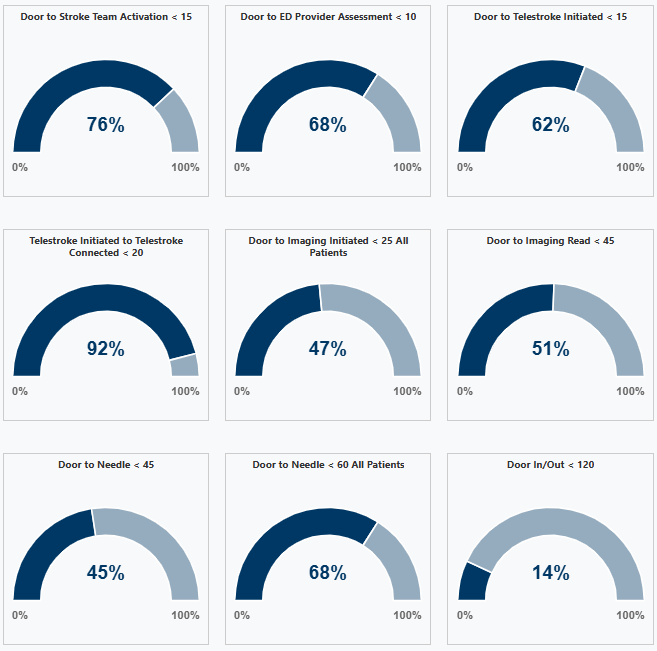
The landing page of the new Minnesota Stroke Portal highlights the new data dashboard, which displays key stroke metrics to support quality improvement tracking.
“I think the recent upgrades to the stroke portal make it exceptionally user-friendly and easy to navigate. The Stroke Dashboard is impressive, it’s great being able to see a snapshot of key metrics on login and I appreciate being able to customize by facility, time period, etc. Overall, the new features make the portal much more efficient.” --Elena Utz, CentraCare quality data abstractor
What’s next?
A program journey never ends—it evolves. As needs shift and new opportunities emerge, the program is shaped by the foundation already built and the people committed to the vision. This project strengthened collaboration across state agencies and with external partners. The Minnesota Stroke Program built new connections and is grateful for the opportunity to elevate the work we do to improve stroke care across Minnesota.
The Stroke Program will continue engaging our partners at every step. They will keep celebrating and showcasing their work through the annual Quality Improvement Awards Program. The Stroke Program will ensure meaningful use of data and continue analyzing population-level trends. And as technology rapidly evolves, they remain focused on finding sustainable solutions to meet the financial and operational demands of hosting a statewide registry. Providing this tool—especially for smaller stroke programs with fewer resources—remains a core commitment of MDH.



