Radon
- Radon in Homes
- Radon Testing
- Radon in Real Estate
- Find a Radon Measurement Professional
- Find a Radon Mitigation Professional
- Radon Mitigation Systems
- Financial Assistance
- Radon Resistant New Construction
- Licensing for Radon Professionals
- Radon Licensing System
- Laws, Rules and Standards
- Radon Poster Contest
Related Topics
Environmental Health Division
Radon in Homes
The Minnesota Department of Health (MDH) provides information on radon and how to protect your family's health. MDH recommends that every Minnesota home be tested for radon.

Download a printable version of the brochure:
Radon: Keeping you safe from radon (PDF)
What is radon?
Radon is a colorless and odorless gas that comes from the soil. The gas can accumulate in the home. Radon gas decays into fine particles that are radioactive. When inhaled, these fine particles can damage the lungs. Exposure to radon over a long period of time can lead to lung cancer.
It is estimated that 21,000 people die each year in the United States from lung cancer due to radon exposure. A radon test is the only way to know how much radon is in your home. Radon can be reduced with a mitigation system.
Where does radon come from?
Radon is produced from the natural decay of uranium and radium, found in rocks and soil. Uranium breaks down to radium, and radium eventually decays into the gas radon. Radon gas is in the soil and common throughout Minnesota. Because soil is porous, radon moves up from the soil and into the home. It can then accumulate in the air and become a health concern.
Radon in Minnesota

Radon is a serious public health concern in Minnesota. The average radon level in Minnesota is more than three times higher than the U.S. radon level. This is due to our geology and how our homes are operated. Minnesota homes are closed up or heated most of the year, which can result in higher levels of radon. In Minnesota, more than two in five homes have radon levels that pose a significant health risk.
Is there a safe level of radon?
Any radon level poses some health risk. While it is not possible to reduce radon to zero, the best approach is to lower the radon level as much as possible. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has set the action level at 4 pCi/L (picocuries of radon per liter of air). MDH recommends installing a radon mitigation system when the radon level is at 4 pCi/L or higher. Between 2 and 4 pCi/L, a radon mitigation system can be considered to lower the level as much as possible. For more information about radon levels in your county, please go to MDH’s Radon Data Portal.
Radon and Lung Cancer
Radon health risks
It is the number one cause of lung cancer for non-smokers and the second leading cause of lung cancer in smokers. Your risk for lung cancer increases with higher levels of radon and longer periods of exposure. If you smoke, the combined risk of smoking and radon exposure is much higher.
You can get free support to quit smoking, vaping, or chewing from Quit Partner programs. Visit QuitPartnerMN.com or call 1-800-QUIT-NOW. You can get free coaching, quit medications, and more. Free help is available for Minnesota teens and adults.
Lifetime Risk of Lung Cancer Death from Radon Exposure (per 1,000 people)
| Average Radon Level (pCi/L) | People who never smoked | People who currently smoke | U.S. general population |
|---|---|---|---|
| 20 | 36 | 260 | 110 |
| 10 | 18 | 150 | 56 |
| 4* | 7 | 62 | 23 |
| 2 | 4 | 32 | 12 |
*EPA Action Level. For the U.S. general population who are exposed to 4 pCi/L of radon over a lifetime, it is estimated that 23 out of 1,000 people will die from lung cancer due to the radon exposure.
How radon enters the home
Radon levels can accumulate to high concentrations in the home. This depends on radon levels in the soil (the source), how radon enters the home (pathways), and pressure differences between the outside air and the inside air (air pressure) that drive radon into the home.
- Source - In Minnesota, soil is the main source of radon, where it occurs naturally.
- Pathways - Radon gas enters the home, usually through openings between the soil and the home. These pathways may include cracks in the concrete slab, floor-wall joints, an open sump pit, or a crawl space. (See Common radon pathways image below)
- Air pressure - Differences in air pressure between the home's interior and the soil can pull radon gas into the home through the pathways.
Common radon pathways
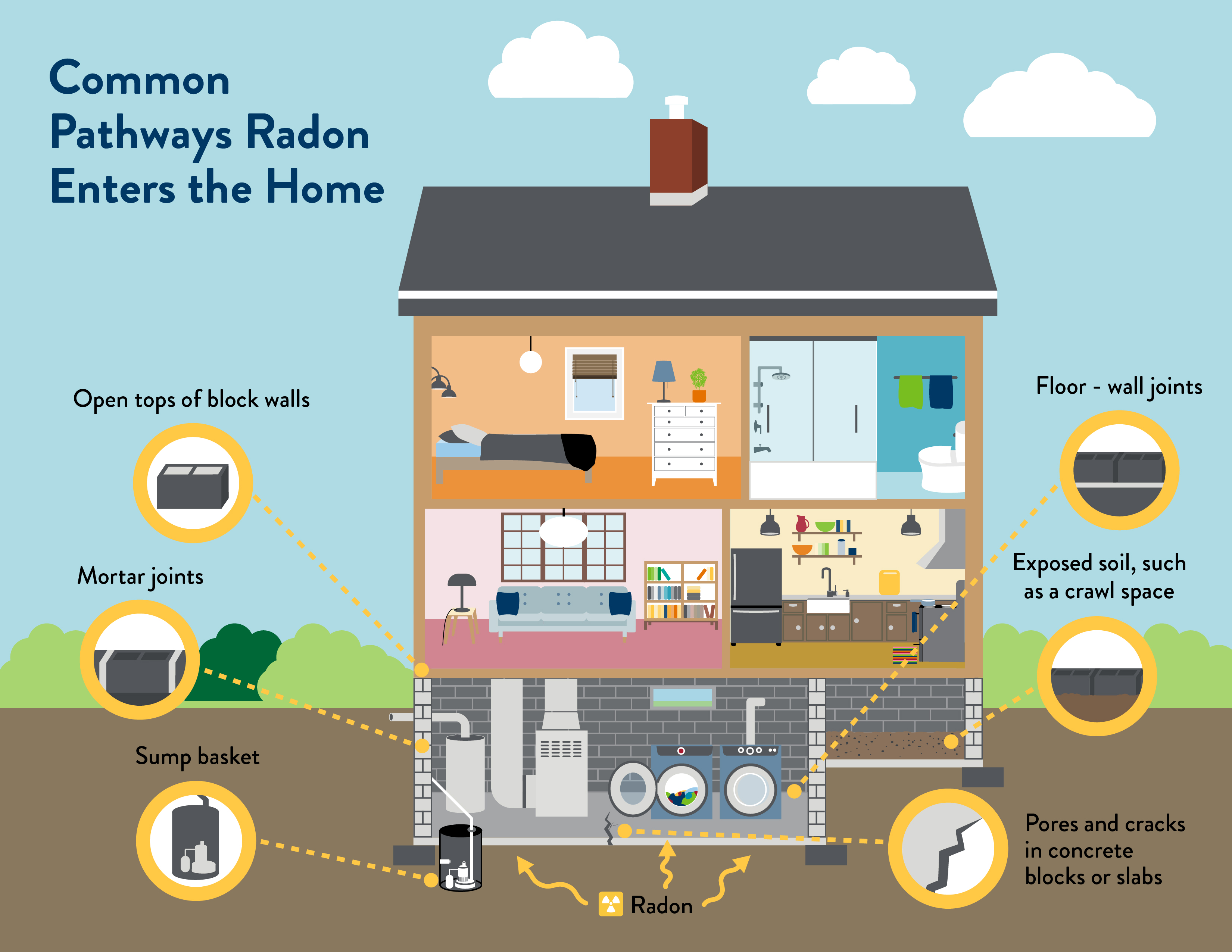
(Click on image above to enlarge)
Air pressure
Homes commonly operate at a lower (negative) pressure compared to the outside air. This pressure difference creates a vacuum and outside air can be pulled into the home through openings like doors and windows. Some of this replacement air comes from the soil. There are three main components contributing to air pressure changes in the home that can bring in radon gas.
 | Stack effect - Warm air rises to the upper portion of the home and is lost to the outside air. Make-up air enters the lower part of the home, and some make-up air comes from the soil. |
 | Down Wind Draft Effect - Strong winds can blow over the top of the home, pushing and pulling air into and out of the house. |
 | Vacuum Effect - Appliances (water heaters, fireplaces, clothes dryers, older furnaces, etc.) and exhaust fans remove air from the home. This can drive soil gas into the home as make-up air enters the lower part of the house. |
Foundations
Any home can have a radon problem, no matter the type of foundation.
 | A basement provides a large surface area in contact with the soil, and radon can enter through different pathways. Taller homes add potential for a greater stack effect. |
 | Homes built slab-on-grade have many openings that allow radon to enter, similar to a basement. |
 | Homes built with crawl spaces are directly connected to the soil and create a pathway for radon to enter the home. |
 | Manufactured homes with solid skirting act like crawl spaces and provide a direct connection to the soil. |
Go to > top
